In modern software development, detecting bugs is just the beginning. The real challenge lies in managing them effectively. A well-structured bug triage meeting ensures that issues are prioritized, assigned, and resolved efficiently, saving time and improving product quality. This step-by-step guide will help teams conduct an effective bug triage meeting, streamline the testing process, and enhance overall software delivery.
For professionals looking to deepen their understanding, enrolling in a Software Testing Course in Pune can provide practical insights into bug management, QA processes, and software lifecycle management.
What is a Bug Triage Meeting?
A bug triage meeting is a structured discussion where newly reported bugs are reviewed, categorized, and prioritized. The main goal is to decide which bugs need immediate attention, which can wait, and which may not require action. By conducting these meetings regularly, teams ensure smooth development progress and maintain high-quality standards.
Objectives of a Bug Triage Meeting:
- Review newly reported bugs.
- Assess severity and impact.
- Assign ownership for resolution.
- Set priorities for development efforts.
- Align QA, development, and management teams on decisions.
Importance of Bug Triage Meetings
Bug triage is more than a procedural step; it’s essential for software quality and team efficiency. Key benefits include:
- Improved Productivity: Developers focus on critical issues first.
- Resource Optimization: Teams allocate time and resources efficiently.
- Backlog Management: Regular triage prevents bug accumulation.
- Clear Communication: Stakeholders stay informed about bug status.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Prioritization is based on severity and business impact, not guesswork.
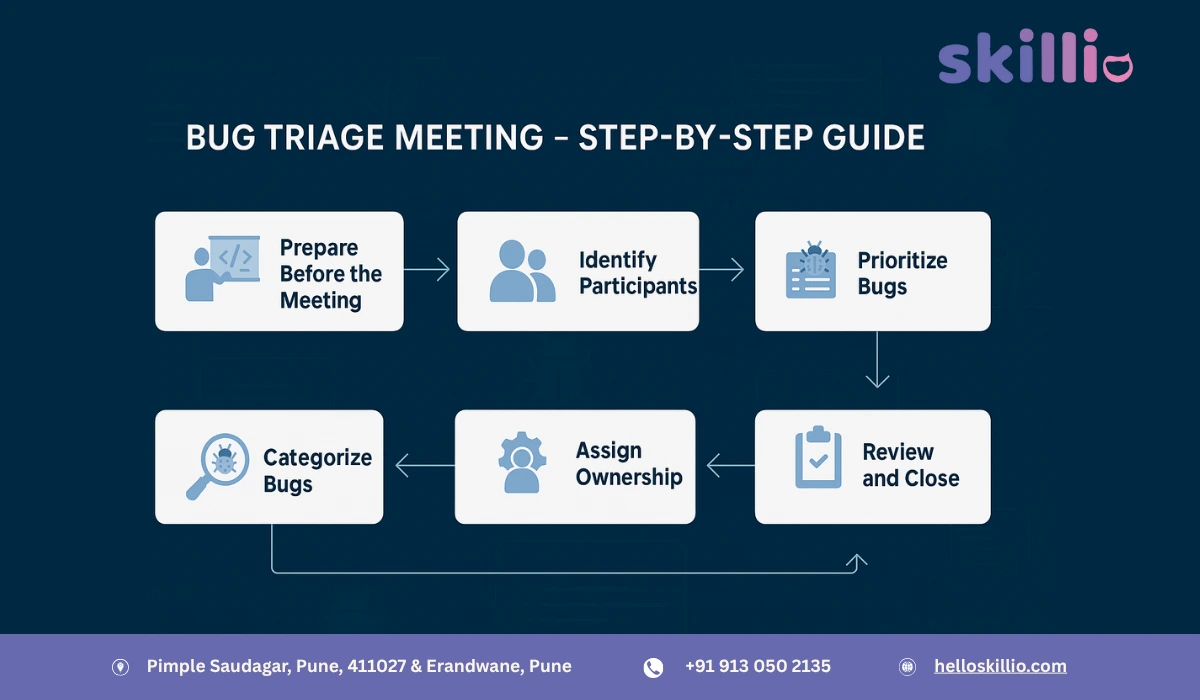
Step-by-Step Guide to Conducting a Bug Triage Meeting
Step 1: Prepare in Advance
Effective triage requires preparation. Gather all relevant information about reported bugs, such as:
- Detailed bug reports from QA testers.
- Screenshots, logs, or replication steps.
- Any history of recurring issues.
- Current workload and sprint schedules.
Using bug tracking tools like JIRA, Bugzilla, or Trello can help consolidate this information efficiently.
Step 2: Identify Participants
Include only the key stakeholders to make discussions focused and actionable:
- QA/Testers: Provide bug details and reproduction steps.
- Developers: Estimate resolution effort and assess technical feasibility.
- Product Managers: Evaluate business impact and user experience implications.
- Project Managers: Ensure alignment with deadlines and resource availability.
The presence of all critical stakeholders ensures informed and balanced decisions.
Step 3: Categorize Bugs
Before prioritizing, categorize each bug to establish clarity:
- Severity: Critical, major, or minor based on functional impact.
- Type: Functional, performance, UI/UX, security, or regression.
- Frequency: How often does the bug occur?
- Impact on Users: Determine which issues affect end-users the most.
Categorization provides a structured approach to decision-making and avoids subjective judgments.
Step 4: Prioritize Bugs
Prioritization ensures that the team addresses high-impact issues first. Typical priority levels include:
- P1 (High Priority): Must fix immediately.
- P2 (Medium Priority): Fix in the upcoming sprint.
- P3 (Low Priority): Can be deferred for future releases.
Combine severity, frequency, and business impact to assign priority. For instance, a minor bug affecting a crucial user workflow may be prioritized higher than a major bug in a rarely used feature.
Step 5: Assign Ownership
Clear ownership prevents ambiguity and ensures accountability. For each bug, define:
- Responsible developer or team.
- Expected resolution timeline.
- Dependencies or potential blockers.
- Required testing or verification steps post-fix.
Step 6: Document Decisions
Documenting outcomes ensures transparency and serves as a reference for future audits:
- Bugs reviewed with severity and priority.
- Assigned owners and expected timelines.
- Any additional instructions or notes.
Bug tracking tools can help update and store decisions efficiently, making follow-up seamless.
Step 7: Review and Close
Before ending the meeting:
- Confirm the priority list with all participants.
- Ensure all bugs have assigned owners.
- Address unresolved issues or disputes.
- Schedule the next triage session for continuity.
A structured review ensures nothing is missed and accountability is maintained.
Best Practices for Effective Bug Triage
- Keep Meetings Short: Limit to 30–60 minutes to avoid fatigue.
- Limit Attendees: Include only those actively involved in decisions.
- Use a Standard Template: Ensures consistency and reduces oversight.
- Base Decisions on Data: Prioritize using severity, impact, and reproducibility.
- Encourage Collaboration: Open communication between QA, development, and management is essential.
- Track Metrics: Monitor bug resolution times, backlog trends, and aging to improve processes.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Skipping preparation, leading to inefficient discussions.
- Including too many participants, causing distractions.
- Ignoring minor bugs, which may escalate if left unresolved.
- Failing to update tracking tools, rendering decisions ineffective.
- Prioritizing based solely on severity without considering user impact.
Tools to Optimize Bug Triage
The right tools streamline bug triage and enhance collaboration:
- JIRA: Comprehensive issue tracking and reporting.
- Bugzilla: Open-source tool with flexible workflows.
- Trello: Visual task management suitable for smaller teams.
- Asana: Combines task and project management with bug tracking.
Real-time updates, notifications, and reporting features improve triage efficiency.
Benefits of Learning Bug Triage in a Software Testing Course
Understanding bug triage and resolution is a critical skill for QA professionals. A Software Testing Classes in Pune can provide hands-on experience with:
- Bug lifecycle management.
- Triage and prioritization techniques.
- Real-world software testing scenarios.
- Use of industry-standard tools like JIRA or Bugzilla.
These skills not only improve professional competency but also increase employability in the competitive IT market.
Conclusion
Conducting an effective bug triage meeting is essential for successful software delivery. By preparing adequately, involving the right stakeholders, categorizing and prioritizing bugs, and maintaining documentation, teams can resolve issues efficiently and maintain high-quality software.
Regular triage sessions, combined with proper tools and processes, help prevent critical bugs from being overlooked, improve resource allocation, and enhance team productivity. For QA professionals aiming to refine these skills, enrolling in a Software Testing Course in Pune can provide valuable practical knowledge and industry insights.
Read Here: Bug in Software Testing: Life Cycle, Detection, and Reporting