Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are transforming industries worldwide, from healthcare and finance to retail and entertainment. At the core of many AI systems is a computational model called a neural network.
Neural networks are inspired by the human brain and are designed to recognize patterns, make predictions, and improve decision-making over time. They are fundamental in applications like image recognition, speech processing, natural language understanding, and autonomous systems.
For students and professionals, understanding neural networks is essential for building a career in AI, data science, or ML. If you are exploring structured learning, enrolling in a Machine Learning Course in Pune can provide you with hands-on experience in building and training neural networks using real datasets and practical projects.
Understanding Neural Networks
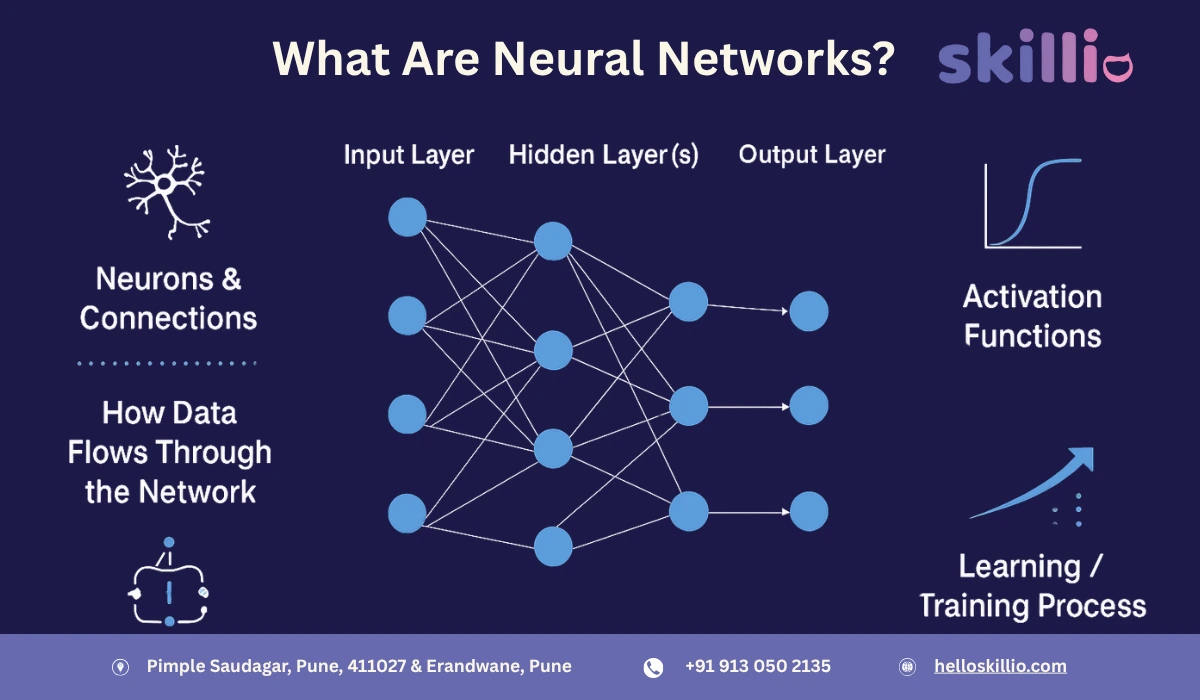
A neural network is a computational model made up of layers of interconnected nodes called neurons. Each neuron processes data, applies mathematical functions, and passes the output to the next layer.
The basic structure of a neural network includes:
- Input Layer: Accepts the raw data for processing.
- Hidden Layers: Perform computations, detect patterns, and extract features.
- Output Layer: Produces predictions, classifications, or decisions.
Neurons are connected with weights and biases, which are adjusted during the training process. An activation function determines whether a neuron should be activated, helping the network learn complex, non-linear patterns.
Neural networks are powerful because they can learn from examples, generalize from patterns, and improve performance over time.
How Neural Networks Work
Neural networks function through two main processes: forward propagation and backpropagation.
- Forward Propagation: Data flows from the input layer through hidden layers to the output layer. Each neuron applies its weights and activation functions to transform the input.
- Backpropagation: The network calculates the error between the predicted output and the actual output. It then adjusts the weights and biases to minimize this error, using optimization techniques like gradient descent.
Example: A neural network trained on handwritten digits can identify numbers even if the handwriting style varies. This ability to learn patterns from examples makes neural networks a cornerstone of AI applications.
Types of Neural Networks
- Feedforward Neural Networks (FNN): The simplest type, where data moves only in one direction—from input to output. Suitable for basic prediction tasks.
- Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN): Specialized for image recognition and computer vision tasks. CNNs use convolutional layers to detect spatial patterns.
- Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN): Designed for sequential data, such as text, speech, or time-series data. RNNs remember previous inputs to make better predictions.
- Deep Neural Networks (DNN): Comprise multiple hidden layers, enabling them to learn highly complex patterns from large datasets.
- Other Variants: GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks) for generating realistic images, autoencoders for feature extraction, and transformers for natural language processing.
Applications of Neural Networks
Neural networks are widely used across industries:
- Computer Vision: Face recognition, medical imaging, autonomous vehicles.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Chatbots, machine translation, sentiment analysis.
- Speech Recognition: Voice assistants like Alexa, Siri, and Google Assistant.
- Finance: Fraud detection, credit scoring, algorithmic trading.
- Healthcare: Disease diagnosis, predictive analytics, drug discovery.
- Recommendation Systems: Personalized recommendations on platforms like Netflix and Amazon.
By understanding neural networks, students and professionals can work on real-world AI solutions and build their career portfolio.
Advantages of Neural Networks
- Pattern Recognition: Detects complex and non-linear relationships in data.
- High Accuracy: Outperforms traditional algorithms in image, text, and speech recognition.
- Adaptable: Improves performance as more data becomes available.
- Versatile: Applicable across multiple domains, from robotics to e-commerce.
- Scalable: Handles large and complex datasets efficiently.
Challenges of Neural Networks
While powerful, neural networks come with certain challenges:
- Data Requirements: Large datasets are needed for effective training.
- Computational Cost: Deep networks require GPUs and high processing power.
- Black Box Nature: It can be difficult to interpret how decisions are made.
- Overfitting: Networks may memorize training data rather than generalize, reducing performance on new data.
Neural Networks vs Traditional Algorithms
| Aspect | Neural Networks | Traditional Algorithms |
| Learning | Learns patterns from data | Follows explicit rules |
| Complexity | Handles complex, non-linear problems | Limited to simpler problems |
| Accuracy | Often higher for large datasets | Can be lower for unstructured data |
| Applications | AI, NLP, Computer Vision | Basic predictions |
Neural networks are essential for modern AI tasks, whereas traditional algorithms are better suited for simpler or structured problems.
Getting Started with Neural Networks
For beginners, starting with neural networks may seem intimidating, but the path is structured and approachable:
- Understand Basics: Learn about layers, neurons, activation functions, and backpropagation.
- Hands-On Practice: Build small projects like image classification or sentiment analysis.
- Use Frameworks: TensorFlow, Keras, and PyTorch simplify network design and training.
- Structured Learning: Enrolling in a Machine Learning Course Training in Pune offers guided learning, real projects, and mentorship from industry experts.
Such courses provide a practical approach, allowing learners to implement neural networks rather than just learning theory.
AI Career Opportunities
AI is a rapidly growing field. Understanding neural networks opens doors to multiple career paths:
- AI Developer
- Data Scientist
- Machine Learning Engineer
- Computer Vision Specialist
- NLP Engineer
For students who want both practical training and job assistance, enrolling in an AI Course in Pune with Placement ensures hands-on learning while preparing for real-world employment. These programs often include portfolio projects, interview preparation, and career guidance.
Future of Neural Networks
The future of neural networks is promising:
- Autonomous Systems: Self-driving cars, drones, and robots.
- Generative AI: AI models that create realistic images, text, and music.
- Healthcare Innovation: Early diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and predictive analytics.
- Business Automation: Enhancing efficiency in finance, logistics, and retail.
By mastering neural networks today, learners can be at the forefront of AI and ML innovation.
Why HelloSkillio is the Right Choice
At HelloSkillio, we provide practical, project-based training in AI and Machine Learning:
- Learn neural networks and other AI models from industry experts.
- Work on live projects to build a professional portfolio.
- Flexible batches suitable for students, working professionals, and career changers.
- Placement support through resume guidance, mock interviews, and company connections.
Whether you choose a Machine Learning Course in Pune or an AI Course in Pune, HelloSkillio ensures you gain the skills, experience, and confidence to succeed in the tech industry.
Conclusion
Neural networks are the backbone of modern AI, powering everything from voice assistants to autonomous vehicles. For learners aiming for a career in AI, understanding neural networks is a must.
Structured courses like a Machine Learning Course in Pune provide hands-on training, mentorship, and real-world experience. With these skills, learners can confidently enter AI, ML, and data science roles, contributing to cutting-edge technologies.
Mastering neural networks not only enhances technical skills but also opens doors to a dynamic and highly rewarding career.
Read Here: How to Work on Live Projects While Learning: Tips for Students